-
1.What is HDMI ?+


What is HDMI ?
HDMI (High Definition Multimedia Interface) means a proprietary audio/video interface transmitting from uncompressed video data, compressed to uncompressed digital audio data through a source device conformed to HDMI. These source devices include display controller, to a conformable computer monitor, video projector, digital TV, and digital audio device. HDMI acts as a digital replacement for analog TV standards.

-
2.What is DisplayPort ?+

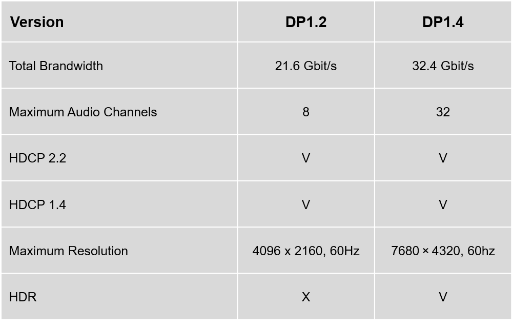
What is DisplayPort ?
Standardized by the VESA (Video Electronics Standards Association), DP (Display Port) is a digital display interface developed by a consortium of PC and chip manufacturers.Initially, the interface connects a video source to a display device (e.g., computer monitor), and can carry audio, USB, and other forms of data.
-
3.What is SDI ?+
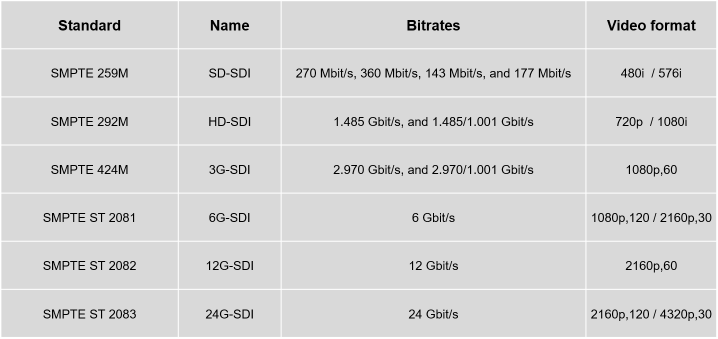
What is SDI ?
SDI (Serial digital interface) is a digital video interface category standardized in 1989 by SMPTE (The Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers). With a formal impedance of 75 ohms, all the various serial digital interface standards use one or more coaxial cables with BNC connectors.
-
4.What is DVI ?+
What is DVI ?
Developed by the DDWG (Digital Display Working Group), DVI (Digital Display Working Group) connects a video source (e.g., video display controller), to a display device (e.g., computer monitor) with the hope of producing an industry standard for the transmission of digital video content.
DVI-I (Integrated; analog and digital). Single link (18+5) or dual link (24+5)
DVI-D (Digital): Single link (18+1) or dual link (24+1)
DVI-A (Analog): Analog signal only (12+5)
-
5.What is VGA ?+
What is VGA ?
VGA (Video Graphics Array) is also called D-sub 15 or mini sub D15. VGA transfers analog signal and is worked on graphics card on computers, monitors and other devices.
-
6.What is YPbPr / YCbCr ?+
What is YPbPr / YCbCr ?
YUV color model is gathered from the rgb model, using luminance and chrominance to represent the color information, making it image processing- competent.
YUV (YPbPr/YCbCr) indicates color difference signals. YPbPr is an analog color difference signal while YCbCr is a digital color difference signal. The processing flow is more straightforward:Analog input signal -> A to D convert -> digital signal -> DSP processing -> digital signal (YCbCr) D to A convert -> analog signal (YPbPr)
-
7.What is RGB ?+
What is RGB ?
RGB model is mixing different wavelengths of light to produce other colors. The initials of the three cumulative primary colors, red, green, and blue form the model name.
-
8.What is EDID ?+

What is EDID ?
Metaformat to display devices to draw their abilities to a video source. Data format is outlined by measurement published by the VESA.EDID data structure contains manufacturer name and serial number, product type, phosphor or filter type (chromaticity data), timings provided by the display, luminance data, pixel mapping data (only for digital displays), and display size.
-
9.What is HDCP ?+

What is HDCP ?
Intel Corporation developed HDCP (High-bandwith Digital Content Protection): a form of digital copy protection, preventing copy of digital audio and video content while travelling across connections.
Types of connections contain DisplayPort, DVI, HDMI, and less popular/deprecated protocols including GVIF (Gigabit Video Interface) and UDI (Unified Display Interface).The system is designed to stop HDCP-encrypted content from playing on impermissible devices that have been altered to copy HDCP content. A transmitting device examines that the receiver is authorized to receive data before sending data. If so, the transmitter encrypts the data preventing the overhearing while it flows to the receiver.
-
10.What is Dolby Digital ?+

What is Dolby Digital ?
Dolby Digital, initially similar with Dolby AC-3, is the name for family of audio compression technologies developed by Dolby Laboratories. Initially called Dolby Stereo till 1995, apart from Dolby TrueHD, the audio compression is lossy according to MDCT (modified discrete cosine transform) algorithm. Dolby Digital's earliest use was to deliver digital sound in cinemas from 35 mm film prints; today, applications include TV Broadcast, radio broadcast via satellite, digital video streaming, DVDs, Blu-ray discs and game consoles.
-
11.Dolby Surround 2.1 / 5.1 / 7.1+

-
12.What is AC-3 ?+

What is AC-3 ?
The MDCT (modified discrete consine transfrom) is the main basis of the Dolby AC-3 multi-channel audio coding standard, a lossy audio compression algorithm.
Dolby Laboratories used the MDCT algorithm together with perceptual coding principles to develop the AC-3 audio format for cinema needs.
-
13.What is DTS ?+

What is DTS ?
DTS, Inc. (initially Digital Theater Systems) is an American company that produces multichannel audio technologies for film and video. In 1993, The company presented it's DTS technology as a rival to Dolby Laboratories, incorporating DTS in the film Jurassic Park (in 1993). The DTS product is used for surround sound formats in both consumer-grade and commercial/theatrical applications. Until 1995, it was known as The Digital Experience. DTS authorizes its technologies to consumer electronics suppliers.
-
14.What is PCM ?+

What is PCM ?
PCM (Pulse-code modulation) is an approach used to digitally define sampled analog signals. It is the common form of digital audio in compact discs, digital telephony, computers and other digital audio applications. The amplitude of the analog signal is tested consistently at uniform intervals in a PCM stream. Each sample is quantized to the closest value in a range of digital steps.
-
15.What is LPCM ?+

What is LPCM ?
LPCM (Linear pulse-code modulation) is a certain type of PCM where the quantization levels are linearly uniform. This is in comparison to PCM encodings where quantization levels differ as a function of amplitude (with the A-law algorithm or the μ-law algorithm). Although PCM is a more general term, it often describes data encoded as LPCM.
-
16.SDVoE+

SDVoE (Software Defined Video-over-Ethernet) is the latest high-performance, software-based AV-over-IP platform that controls and distributes audio visiual systems of a Ethernet/Fiber networks. With SDVoE, programmers, manufacturers and software engineers easily analyze customers' needs in order to build new and interesting applications.
Switching and distribution are commoditized by Ethernet as the AV industry inevitably transitions to IP-based solutions. How do AV manufacturers add value? Creating powerful endpoint processors and software applications are key. Endpoints that convert between AV signals (HDMI) and Ethernet contain processing engines that reformat and reconstruct audio and video signals as needed (scaling to a display; putting up a video wall; downmixing audio, etc.).
The software that creates user experiences by telling those endpoints what to do is the other area ripe for innovation.
SDVoE technology is the standardized interface between the endpoints and the software, providing the momentum to create new classes of applications.
SDVoE technology is:
The most widely adopted networked AV standard in the industry, delivering HDMI over Ethernet with zero latency
The only turnkey solution for zero-latency AV over IP available to AV equipment manufacturers
A full stack solution, clearly specifying an approach to every layer of the OSI network model, from the physical infrastructure to an application programming interface (API).
A comprehensive API that provides a simple interface to control complex tasks like video wall processing, image compositing, video routing, scaling, aspect ratio management, audio downmixing, and much more.
-
17.What is HDbaseT?+

HDBaseT is fully HDMI-compliant. HDBasetT connects commercial, industrial, and CE devices and AV receivers to compatible digital audio devices, computer monitors, multi-touch displays, digital televisions, and digital video projectors.
HDBaseT Technology stands out with it's 5 Play feature set. The 5 Play feature set focuses on audiovisual (AV), Ethernet, USB, Control Signals, and Power-over-HDBaseT (PoH).
-
18.HDbaseT video support+
HDbaseT supports uncompressed video to a network of devices or as a point-to-point to accurately render gaming graphics and features. Supports TV and PC video formats (e.g., standard, enhanced, high-definition, Ultra-HD and 3D video).
HDBaset 1.0 and 2.0 support uncompressed video up to:
4K at 30Hz with 8-bit 4:4:4 color coding,
4K at 30 Hz up to 12-bit 4:2:2 and high dynamic range (HDR),
4K at 30 Hz with Dolby Vision standard mode,
4K at 60 Hz with 8-bit 4:2:0 color coding.
HDBaseT 3.0 supports uncompressed video up to:
4K at 60Hz with 8-bit 4:4:4 color coding,
4K at 60 Hz up to 12-bit 4:2:2 and high dynamic range (HDR),
4K at 60 Hz with Dolby Vision standard mode.
-
19.HDbaseT Audio support+
HDMI carries audio without the need for multiple cables, supporting all standard HDMI audio formats (e.g., either compressed or uncompressed 32 channels of high-resolution 24-bit 192kHz audio, or 2-channel audio with a sampling frequency up to 1.536MHz).
HDBaseT 2.0 supports separate bi-directional S/PDIF audio that was introduced with the HDMI 1.4 specification, the upstream channel of which can optionally be used to carry HDMI Audio Return Channel.
With bandwith increase, HDBasetT 3.0 provides optional support HDMI enhanced Audio Return Channel (eARC), for all of the same audio formats upstream already available in the main HDMI downstream signal ( e.g., immersive and object-based audio such as Dolby Atmos or DTS).
-
20.Near zero latency+
The specification allows for negligible latency: less than 10 microseconds (.01 milliseconds) over 100m of cable. For example, a 60hz refresh rate means a full image is displayed after 16.67 ms. Adding 0.01 ms is only a 0.06% increase in the signal latency.
-
21.Ethernet support+
HDBaseT 1.0 and 2.0 supports the 100 Mbit/s version of Ethernet over twisted pair. This provides Internet access to devices such as CE devices, computers, and smart TVs to communicate with each other and access multimedia content on the local network. HDBaseT 3.0 increases this capability to 1000 Base-T (Gigabit) Ethernet.
-
22.USB support+
HDBaseT 2.0 supports for USB 2.0, with a capacity for the simultaneous connection of up to 7 USB devices and a transfer rate up to 190 Mb/s. HDBaseT 3.0 increases this to 350 Mb/s. -
23.Control signals+
HDBaseT delivers HDMI Consumer Electronics Control (CEC) protocol signals that control basic functionality such as power-on, power-off and play/stop, along with RS232 and consumer IR (remote control) commands.
-
24.PoH (Power over HDbaseT)+
HDBaseT provides power-over-HDBaseT (PoH), provisioning up to 100 W of operating DC power to CE devices, such as monitors and TVs. If a display is enabled as a 100W powered device (PD), and is connected to a matching PoH transmitter (power sourcing equipment, PSE), the display will be able to draw its operating power through the HDBaseT link, not requiring a separate power connection.

